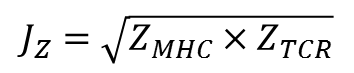Introduction: |
What can PAcomplex do for you? |
The PAComplex is a novel peptide antigen search server that is useful for analyzing novel peptide antigens and inferring homologous peptides. To our best knowledge, PAComplex is the first web server investigating both peptide-MHC and peptide-TCP interfaces to infer peptide antigens and homologous peptide antigens of a query from complete pathogen genome databases and experimental peptide databases. For a query, PAComplex shows the detailed atomic interactions, binding models, homologous peptide antigen, joint Z-value of each peptide candidate. On the other hand, most of the current peptide-antigen prediction web servers only provide ranks and scores of the query protein sequence or peptides except the MODPROPEP server (Table 1).
Table 1. Comparing PAComplex with four web servers for MHC-peptide interactions
| Features |
PAComplex |
SYFPEITHI |
SVMHC |
PREDEP |
MODPROPEP |
| Input format |
Protein sequence / Peptide sets |
Protein sequence |
Protein sequence / Swiss-Prot AC/ID / RefSeq ID |
Protein sequence |
Protein sequence / Peptide sets |
| Technique / Algorithm |
Template-based model and Homologous search |
Motif pattern |
Machine learning |
Protein sequence / Peptide sets |
Protein sequence / Peptide sets |
| Peptide-MHC |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| Peptide-TCR |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
No |
| Cutoff of prediction |
Yes (Joint Z-value ≥ 4) |
No |
Yes (Score > 0) |
No |
No |
| Binding model visualization |
Yes |
No |
no |
No |
Yes |
| Interacting type |
Hydrogen bonds and VDW forces |
No |
no |
No |
No |
| Homologous peptides |
Yes |
No |
no |
No |
No |
| Detabase search |
Yes |
No |
no |
No |
No |
|
|
Input Format: |
| There are two ways to submit data for prediction. Sequence can be pasted in Fasta format or listed by specific length of peptides.
|
|
| The inputted sequence is in FASTA format consists of a single-line description, followed by lines of sequence data. The first character of the description line is a ">" symbol in the first column. For example: |
|
>sp|P03155|DPOL_HBVD1 Protein P (Fragment) OS=Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype adw (isolate United Kingdom/adyw/1979) GN=P PE=1 SV=1
MPLSYQRFRRLLLLDDEAGPLEEELPRLADEDLNRRVAEDLNLGNLNVSIPWTHKVGNFT
GLYSSTVPVFNPHWKPPSFPNIHLHQDIIKKCEQFVGPLTVNEKRRLKLIMPARFYPNFT
KYLPLDKGIKPYYPEHLVNHYFQTRHYLHTLWKAGVLYKRVSTHSASFCGSPYSWEQELQ
HGAESFHQQSSGILSRPPVGSSLQSKHQQSRLGLQSQQGHLARRQQGRSWSIRARVHPTA
RRPFGVEPSGSGHNANLASKSASCLYQSPVRTAAYPAVSTSENHSSSGHALELHNLPPNS
ARSQSERPVFPCWWLQFRDSKPCSDYYLSHIVNLLEDWGPCAEHGEHHIRIPRTPARVTG
GVFLVDKNPHNTAESRLVVDFSQFSRGNYRVSWPKFAVPNLQSLTNLLSSNLSWLSLDVS
AAFYHLPLHPAAMPHLLVGSSGLSRYVARLSSNSRIINHQHGILQNLHDSCSRNLYVSLL
LLYKTFGWKLHLYSHPIILGFRKIPMGVGLSPFLLAQFTSAICSVVRRAFPHCLAFSYMD
DVVLGAKSVQHLESLFTAVTNFLLSLGIHLNPNKTKRWGYSLNFMGYVIGCWGSLPQDHI
IHKIKECFRKLPVHRPIDWKVCQRIVGLLGFAAPFTQCGYPALMPLYACIQSKQAFTFSP
TYKAFLCKQYLNLYPVAEQRPGLCQVFADATPTGWGLVMGHQRMRGTFLAPLPIHTAELL
AACFARSRSGANILGTDNSVVLSRKYTSFP
|
|
|
| A list consists of specific length peptide in single letter code. For example: |
|
ALWGFFPVL
SLLMWITQV
GILGFVFTL
RLWHYPCTI
SIVAYTMSL
DLMGYIPAV
IMSSFEFQV
ALWDSNFFT
CNYSKFWYL
YLVIYLNRT
MQWLTQYYI
|
|
Scoring function: |
Joint Z-value |
To evaluate the complex similarity between TCR-pMHC and TCR-p'MHC, we define the joint Z-value (Jz) as:
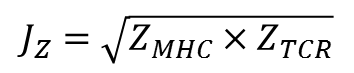
The ZMHC and ZTCR of a TCR-p'MHC candidate with interaction score (E) can be calculated by (E¡V£g)/£m where £g is the mean and £m is the standard deviation from 10,000 random interfaces. For a TCR-pMHC template collected from Protein Data Bank (PDB), these 10,000 random interfaces are generated by substituting with another amino acid according to the amino acid composition derived from UniProt. |
|
Knowledge-based scoring matrices for peptide-MHC interactions |
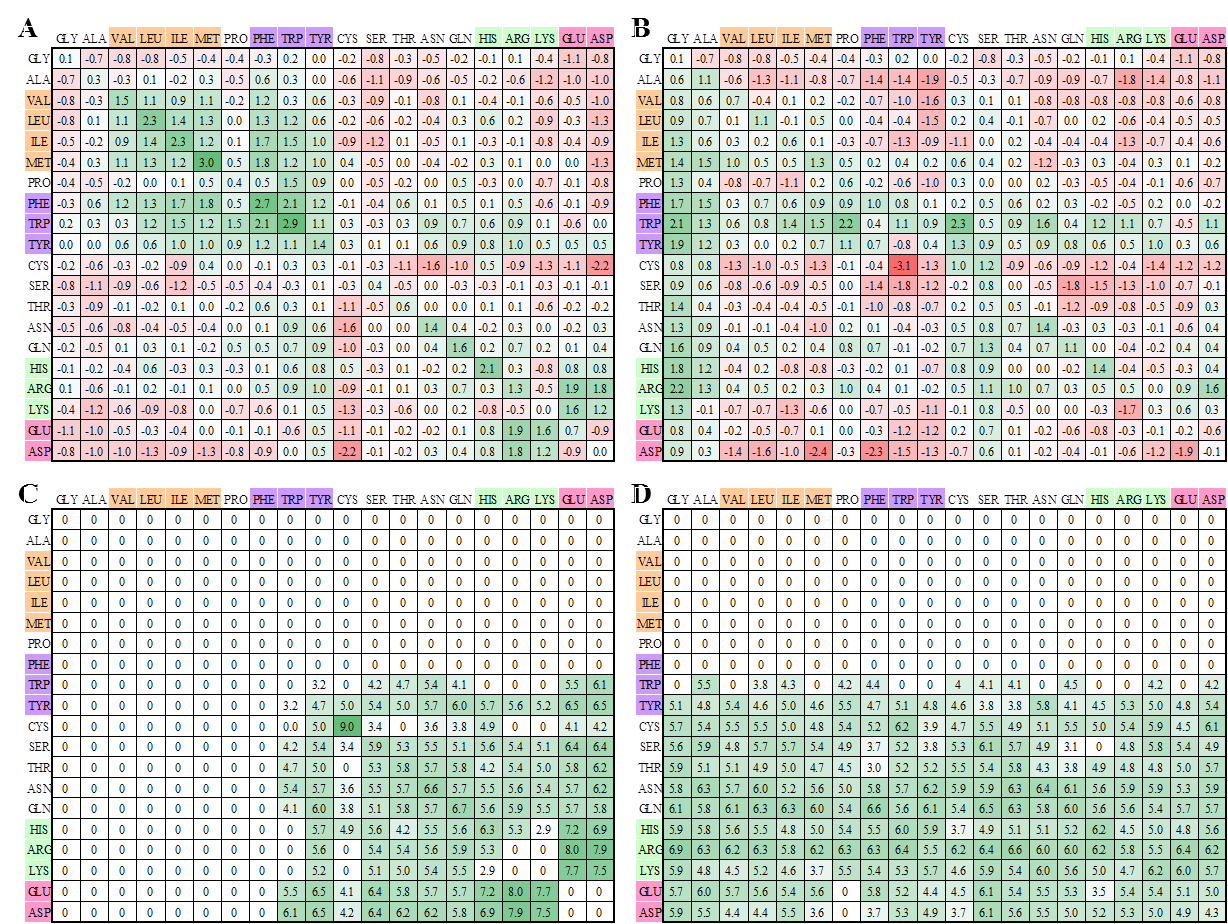 |
|
Knowledge-based peptide-MHC interacting scoring matrices: (A) sidechain-sidechain van-der Waals scoring matrix; (B) sidechain-backbone van-der Waals scoring matrix; (C) sidechain-sidechain special-bond scoring matrix; (D) sidechain-backbone special-bond scoring matrix. The sidechain-sidechain scoring matrices are symmetric and sidechain-backbone scoring matrices are nonsymmetric. For sidechain-sidechain van-der Waals scoring matrix, the scores are high if large-aliphatic residues (i.e. Val, Leu, Ile, and Met) interact to large-aliphatic residues or aromatic residues (i.e. Phe, Tyr, and Trp) interact to aromatic residue. In contrast, the scores are low when nonpolar residues interact to polar residues. For sidechain-sidechain special-bond scoring matrix, the scores are high when an interacting resides (i.e. Cys to Cys) form a disulfide bond or basic residues (i.e. Arg, Lys, and His) interact to acidic residues (Asp and Glu). The scoring values are zero if nonpolar residues interact to other residues.
|
|
Knowledge-based scoring matrix for peptide-TCR interactions |
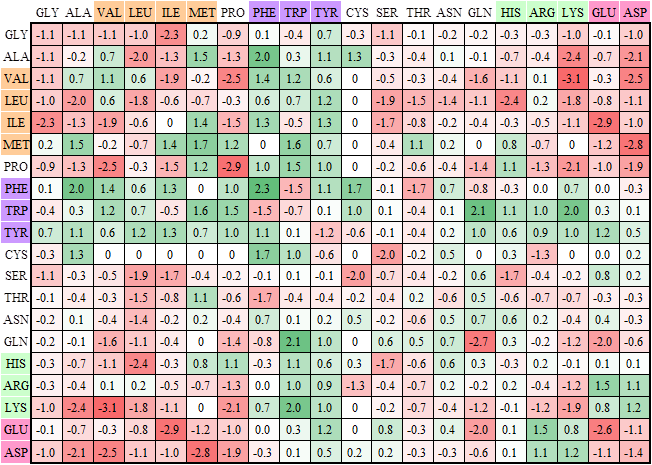 |
|
This matrix is a residue-based matrix derived from a non-redundant set which consists of 62 structural antigen-antibody complexes constructed by Ponomarenko et al. The interface prefers aromatic residues (i.e. Phe, Trp, and Tyr), which interact with aliphatic residues (i.e. Ala, Val, Leu, Ile, and Met) or long side-chain polar residues (i.e. Gln, His, Arg, Lys, and Glu), to form strong van der Waals forces (yellow boxes). Additionally, the scores are high if basic residues (i.e. Arg and Lys) interact with acidic residues (i.e. Asp and Glu). In contrast, the scores are low (purple box) when nonpolar residues interact to polar residues.
|
|